Understanding the 3 Types of Employee Engagement and How to Improve Them

A Global Employee Recognition and Wellness Platform
When most people think about employee engagement, the conversation often revolves around levels, whether an employee is fully engaged, partially engaged, or disengaged. While this is a common approach, it’s an oversimplification of the concept.
The current state of employee engagement is evident in Gallup’s survey, which found that only 21% of employees worldwide are engaged at work. However, there’s more to employee engagement than just how much someone is engaged. To truly understand engagement, we need to look beyond these levels and explore the types of engagement employees experience.
- Is the employee cognitively engaged, thinking deeply about their tasks and the organization’s mission?
- Are they emotionally engaged, forming a connection to the company’s values and culture? or
- Are they behaviorally engaged, consistently showing up through actions and productivity?
In this blog, we’ll dive into these different types of employee engagement, viz., cognitive, emotional, and behavioral, and explore how they manifest in the workplace. Understanding these engagement types will allow HR leaders to create more effective and targeted strategies for fostering engagement.
If you’re interested in understanding the levels of engagement first, check out our Levels of Employee Engagement blog for a more in-depth look.
Key Insights
- Concept of Employee Engagement Types
- Definitions of each type of employee engagement
- Examples of each type of employee engagement
- How HR Can Improve Different Types of Employee Engagement
What Does “Type of Engagement” Actually Mean?
When we talk about types of engagement, it’s essential to distinguish it from levels of engagement. While levels describe how much someone is engaged (fully, partially, or not at all), types refer to what kind of effort or involvement an employee brings to their work.
Think of it like this: An athlete may be physically engaged in their training, but they might not feel emotionally connected to the sport. The physical effort is there, but the emotional investment isn’t. This shows us that engagement isn’t one-dimensional. It’s multi-faceted and influenced by how employees think, feel, and behave.
To break it down further, engagement types can be grouped into two key areas:
-
Modalities: How engagement is expressed. This refers to what engagement looks like- cognitive (thinking), emotional (feeling), and behavioral (acting).
-
Levels/Personas: How engagement shows up in specific roles or employees. This refers to the degree of engagement, whether an employee is actively engaged, passively engaged, or disengaged.
By understanding both the types and levels of engagement, HR leaders can gain a much deeper understanding of employee motivation and create more effective strategies.
The 3 Types of Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is multi-dimensional. Beyond just how much someone is engaged, we need to understand what type of engagement they are experiencing. The following are the three primary types of employee engagement:
1. Cognitive Engagement

Cognitive engagement revolves around the intellectual investment an employee makes in their work. Employees who are cognitively engaged approach their work thoughtfully and strategically, constantly seeking to improve and innovate.
Cognitive engagement can be defined as the mental effort employees put into understanding their roles, the tasks they perform, and the organization’s mission. It involves a deep intellectual connection to work, where employees are not only aware of what they’re doing but also why they’re doing it and how it impacts the larger picture.
When employees are cognitively engaged, they’re more likely to think critically about their work, leading to greater innovation and problem-solving. This type of engagement also helps employees align their efforts with company objectives, making them more efficient and effective contributors.
Research published in the International Journal of Training Research shows that talent-based training and perceived organizational support positively influence cognitive engagement, which in turn enhances individual performance.
Examples of Cognitive Engagement
- An employee who proactively learns new skills to adapt to the company’s evolving needs.
- A team member who dives deep into data to discover insights that lead to improved decision-making.
- A worker who constantly questions how processes can be improved, seeking out opportunities for innovation.
2. Emotional Engagement

Emotional engagement is about the emotional connection employees have to their work. Employees who are emotionally engaged are deeply invested in the company’s mission, culture, and values. They feel a sense of belonging and pride in their work.
Emotional engagement can be defined as the emotional attachment an employee has to their role, the team, and the organization. Employees who are emotionally engaged are motivated by more than just a paycheck; they are driven by a sense of purpose and alignment with the company’s mission.
Employees who are emotionally engaged are more likely to be satisfied with their roles and remain with the organization long-term. This connection often leads to higher retention rates, as employees feel valued and connected to their work.
Examples of Emotional Engagement
- An employee who feels a sense of pride in contributing to a project that aligns with their personal values.
- A team member who shows enthusiasm for company events and team-building activities, fostering camaraderie.
- A worker who goes above and beyond, not because they have to, but because they genuinely care about the outcome.
3. Behavioral Engagement

Behavioral engagement is the observable actions employees take that reflect their commitment to their role and the organization. It’s about what employees do in the workplace, whether they participate in meetings, take on new challenges, or consistently meet performance expectations.
Behavioral engagement can be defined as the actions employees take that show their involvement. It’s measurable and visible. Employees who are behaviorally engaged contribute actively to the team’s success. They demonstrate commitment through consistency, accountability, and productivity.
Examples of Behavioral Engagement
- An employee who volunteers to take on leadership roles or additional responsibilities.
- A team member who actively participates in brainstorming sessions, offering constructive ideas and solutions.
- A worker who consistently meets deadlines and exceeds performance expectations, taking ownership without needing micromanagement.
Now, let’s take a look at some other notable types of employee engagement below.
Physical Engagement
First introduced by William Kahn in his seminal 1990 paper, Psychological Conditions of Personal Engagement and Disengagement at Work, physical engagement pertains to the physical energy and effort employees invest in their roles. Kahn emphasized that individuals can engage varying degrees of their physical selves in their work, influencing their performance and satisfaction.
Examples of Physical Engagement:
- An employee who consistently arrives on time, participates actively in meetings, and approaches tasks with vigor.
- A team member who volunteers for additional responsibilities, demonstrating a proactive attitude.
- An individual who maintains a high level of energy throughout the workday, even during challenging projects.
Social Engagement
Social engagement has been recognized in contemporary HR literature as a critical component of overall employee engagement. It refers to the quality of interpersonal relationships and the sense of community within the workplace.
Social engagement encompasses the interactions, relationships, and sense of community employees experience at work. It reflects how connected individuals feel to their colleagues and the organization as a whole.
Examples of Social Engagement:
- An employee who actively participates in team-building activities and social events.
- A team member who collaborates effectively, shares knowledge, and supports colleagues.
- An individual who feels a strong sense of belonging and camaraderie within the workplace.
Common Levels of Engagement
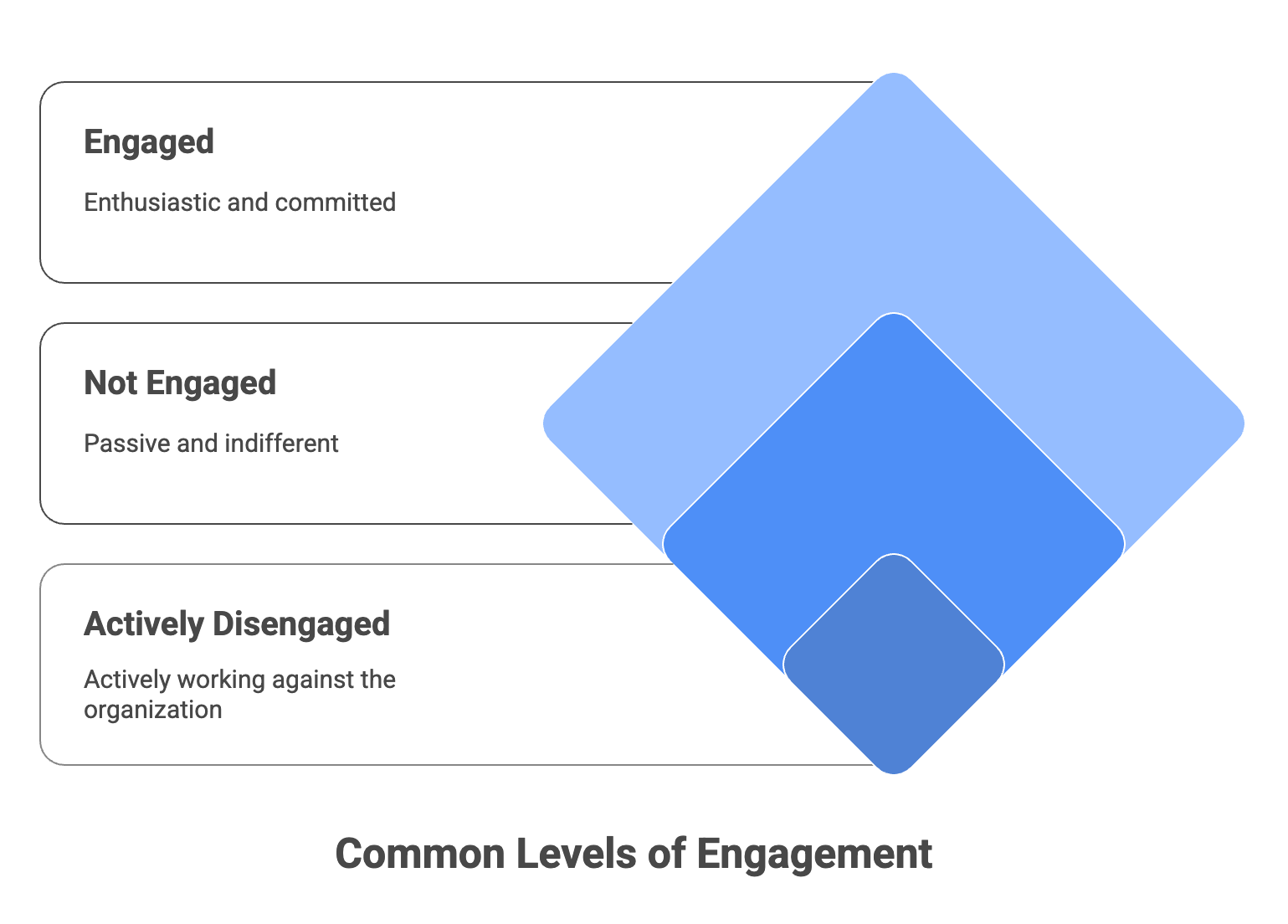
While the types of engagement help us understand how employees connect with their work, levels of engagement describe the depth of those connections.
Most organizations use a three-tiered model to classify employee engagement levels. These levels are especially useful when analyzing survey data or designing engagement programs at scale.
1. Engaged
These employees are highly involved in their work and deeply connected to the organization. They bring energy, enthusiasm, and purpose to what they do. Engaged employees don’t just complete tasks; they take ownership, suggest improvements, and often act as informal leaders within their teams.
Signs of an Engaged Employee:
- Proactively contributes to team discussions and initiatives
- Seeks growth opportunities and takes pride in their work
- Feels aligned with the company’s mission and culture
2. Not Engaged
These employees do what is expected of them, nothing more, nothing less. They’re often described as being checked out or coasting through their workday. They may not be unhappy, but they lack motivation and emotional connection to their work.
Signs of a Not Engaged Employee:
- Delivers work on time but rarely shows initiative
- Avoids taking risks or going beyond the basics
- Doesn't strongly identify with the organization’s goals
3. Actively Disengaged
These employees are disconnected and often dissatisfied. They may feel undervalued, unsupported, or misaligned with the organization. Worse, their discontent can spread to others, hurting morale and productivity.
Signs of an Actively Disengaged Employee:
- Vocal about frustrations without seeking solutions
- Resistant to change and new initiatives
- Withdraws from collaboration or undermines team cohesion
Connecting Levels and Types of Engagement
While levels give us a sense of intensity, types tell us about the nature of engagement. For example:
- An engaged employee may exhibit strong cognitive, emotional, and behavioral engagement simultaneously.
- A not engaged employee may still demonstrate behavioral engagement (showing up and doing the work) but lack emotional investment.
- An actively disengaged employee might disengage across all types—or in one key area, such as emotionally, while still going through the motions behaviorally.
To visualize this, consider a grid that maps engagement types against levels. This can help HR teams better interpret survey results and identify what kind of support or intervention each group needs.
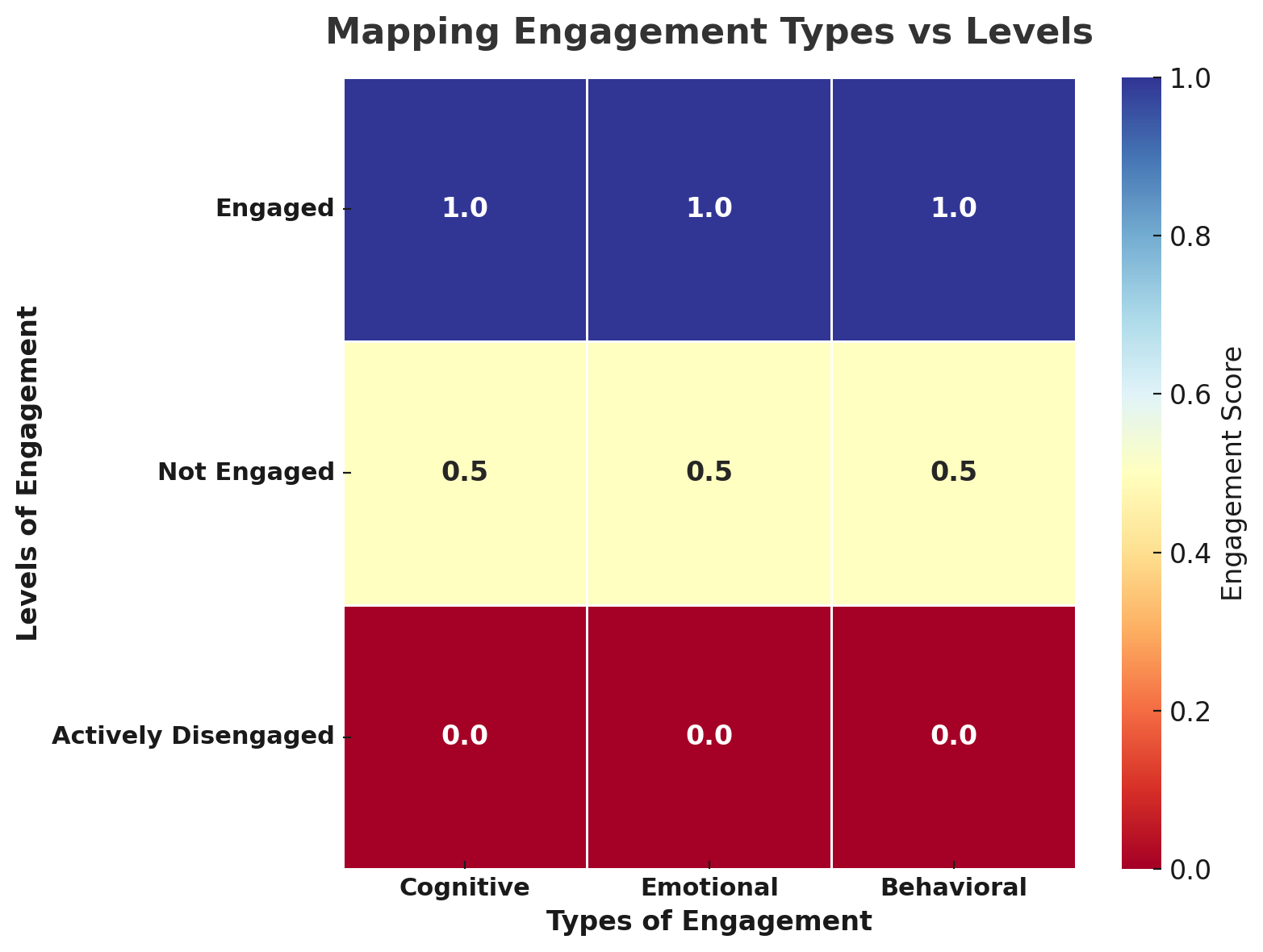
This chart maps engagement levels across cognitive, emotional, and behavioral dimensions. Engaged employees demonstrate strong commitment in all three areas, while those who are not engaged show only moderate involvement, and actively disengaged employees score the lowest. It’s a simple way to see how deeply connected employees are to their work and organization.
How HR Can Improve Different Types of Employee Engagement
Once we understand the types of employee engagement, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral, HR leaders can implement tailored strategies to foster each type. By recognizing where employees may be lacking in engagement and taking actionable steps, HR can create a more motivated, productive, and loyal workforce.
This section will break down each type of engagement and provide practical strategies for HR to improve it.
1. Cognitive Engagement
What It Means
Cognitive engagement refers to the mental investment employees make in their work. It’s about how much thought, critical thinking, and innovation employees apply to the tasks they perform.
Signs of Low Cognitive Engagement
- Employees lack initiative and only complete tasks without much thought.
- There is a noticeable lack of problem-solving or innovation in their approach.
- Employees show little curiosity or interest in learning and developing new skills.
How HR Can Improve Cognitive Engagement
- Provide Opportunities for Learning and Development: Offering employees the chance to expand their knowledge and skills through formal training, workshops, or on-the-job learning experiences shows that you’re invested in their growth.
- Encourage Curiosity and Exploration: Fostering a culture where employees are encouraged to ask questions and think creatively can spark new ideas and approaches. Leaders should support exploration and challenge the status quo.
- Recognize and Reward Intellectual Contributions: Recognizing employees for their innovative ideas or strategic thinking reinforces the importance of cognitive engagement. Public acknowledgment or tangible rewards can motivate others to take a more thoughtful approach to their work.
Source: Vantage Recognition
2. Emotional Engagement
What It Means
Emotional engagement refers to the emotional connection an employee has with their work and the organization. It’s about how much employees care about their tasks, the company’s mission, and their colleagues.
Signs of Low Emotional Engagement
- Employees seem disconnected or apathetic toward the company’s mission.
- There is a lack of enthusiasm or pride in the work they do.
- Employees don’t participate in team activities and seem disengaged from their colleagues.
How HR Can Improve Emotional Engagement
-
Foster a Positive and Supportive Work Environment: Create a workplace culture that prioritizes support, inclusivity, and recognition to help employees feel valued.
-
Create a Sense of Belonging and Community: Encourage teamwork and collaboration within the organization. Employees are more likely to feel emotionally connected when they feel part of something bigger.
-
Recognize Employee Milestones: Celebrating employee milestones, whether personal or professional, reinforces their emotional connection to the company.
Source: Vantage Recognition
3. Behavioral Engagement
What It Means
Behavioral engagement refers to the actions employees take to demonstrate their involvement in their work. It’s not just about how they feel or think but how their actions translate into productivity and collaboration.
Signs of Low Behavioral Engagement
- Employees meet the minimum expectations but don’t go beyond that.
- There’s a lack of initiative or ownership over tasks.
- Employees rarely take on new challenges or engage in teamwork and collaboration.
How HR Can Improve Behavioral Engagement
- Align Employee Goals with Organizational Objectives: Ensure that employees understand how their work contributes to the company’s larger mission.
- Provide Challenging and Meaningful Work: Offering employees purposeful tasks that challenge their abilities keeps them engaged.
- Empower Employees to Make Decisions: Giving employees autonomy over their work inspires greater engagement as they feel trusted and responsible for their outcomes.
By understanding the different types of engagement and implementing these strategies, HR leaders can create a more engaged and high-performing workforce. Each engagement type influences productivity, morale, and employee retention, so focusing on the specific needs of each type will lead to stronger organizational outcomes.
In The End
Understanding the different types of employee engagement, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral, helps HR leaders tailor strategies that boost employee motivation and productivity. By focusing on each type, HR can foster critical thinking, emotional connection, and proactive behaviors, all of which drive better performance and retention.
When employees are engaged in all these areas, they are more likely to feel valued, stay longer with the company, and contribute meaningfully to organizational success. A comprehensive approach to engagement is key to creating a thriving workforce and achieving long-term growth.

















